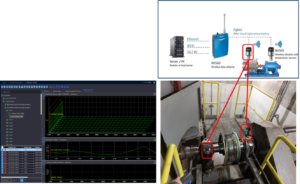
Comparison between AC electric motor inspection techniques
This article makes a comparison between AC electric motor inspection techniques, with these in service and stopped.
What does electric motor analysis technology consist of? e-MCM and Artesian
MCM is a recent electric motor analysis technology, that works based on artificial intelligence that compares the actual engine to be monitored, with a mathematical model of the engine, running up to 600 different load conditions. This mathematical model is obtained from a learning period lasting a few days.

This technology was developed for NASA to make the condition control of the main engine of the Space Shuttle.
The diagnostic monitoring system MCM is also designed to detect electrical faults in engines, in response to limitations of vibration monitoring. In addition to the electrical failure modes, also detects mechanical failure modes the engine or driven machinery. Emerges as the only alternative in situations where vibration monitoring is not practical dedicated, economic or comprehensive enough. You can detect changes in the load the motor is facing due to abnormalities in the driven equipment or process, as cavitation or clogged filters and screens.
e-MCM features
Digital engine modeling
Artesis technology creates a virtual replica of the engine, continually updated with real-time data. This digital twin enables simulation and analysis of engine performance, providing accurate fault detection and actionable operational recommendations.
Continuous monitoring
The system collects data continuously and in real time, detecting faults with up to 6 months in advance. This guarantees high operational reliability, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing unexpected downtime.
Pump performance monitoring
Artesis technology monitors pumping groups, analyzing critical parameters, such as flow rates and pressure. This feature ensures optimal pump performance and early detection of potential problems.
Efficiency and cost analysis
By identifying inefficiencies, helps users optimize performance and achieve significant savings, such as reducing 10% in the maintenance costs of pumping groups.
Automatic diagnosis
Leveraging machine learning, Artesis automatically identifies faults and provides useful information. This reduces the need for manual analysis, enabling faster, data-driven decision-making for maintenance and repairs.
3 Tests with engine in service vs.. stopped
- Test in operation
- Monitoring with the equipment connected and in operation
- Real-time fault detection (e.g., the Artesis system detects faults with up to 6 months in advance).
- Ideal for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Methods with the engine stopped
- Test equipment when turned off, usually during scheduled stops.
- Useful for detailed diagnostics, as reactive rather than continuous approaches.
- Conclusion:
- Although offline tests are useful for detailed diagnostics, are reactive and not continuous.
- Continuous monitoring and digital engine modeling aligns with online/powered testing, enabling real-time insights without stopping equipment.
- Auto Diagnostics leverages machine learning to analyze data in real time, a key benefit in online scenarios.
4 Types of essays
With the engine running
- Defects in rotor bars: Detected via current signature analysis, which identifies irregularities in the rotor current.
- Bearing wear, misalignment and other mechanical failures
- Eccentricity: Frequency domain patterns in the current signal reveal problems in the air gap between the rotor and stator.
- Performance Issues: Monitor THD, power quality and efficiency problems by analyzing the current spectrum and correlating it with energy consumption.
- Limitation: Unable to detect static faults, such as open circuits or insulation degradation, no operational context.
With the engine stopped
- Insulation Test (AND): Identifies weaknesses: insulation degradation, moisture or contamination in the windings, cracks or holes in the insulation
- Dielectric Absorption Ratio Test (BUT): Similar to the IR test; evaluates the polarization capacity of the insulation, providing additional information about your condition.
- Surge Test (Surge Test): Detects insulation faults between turns (spiral to spiral), between coils (coils of coils), and between phases (fase a fase) in the motor windings.
- Winding Test: Measures the resistance of motor windings to detect electrical imbalances or faults.
- Rotor Influence Check (RIC): Evaluates the condition of the rotor by examining its influence on the stator windings. (Variations in inductance as the rotor moves indicate anomalies.)
Comparison of test results
| Type of Failure | Category | Test in operation | Teste Desenergizado |
| Defects in rotor bars | Electrical | Sim | No |
| Fault in Stator Winding Insulation | Electrical | Partial (current analysis detects operational impacts) | Sim (insulation test) |
| Short-circuited stator turns | Electrical | Sim (ESA) | Sim (surge test) |
| Open Circuits | Electrical | No | Sim (continuity test) |
| Loose connections | Electrical | Partial (intermittent operational problems via ESA) | Sim (visual inspection, continuity test) |
| Bearing wear | Mechanics | Sim (ESA) | Limited (visual inspection, only in severe cases) |
| Misalignment | Mechanics | No | |
| Imbalance | Mechanics | No | |
| Eccentricity | Mechanics | No | |
| Harmonic Distortion | Operational | Sim | No |
| Power Quality Issues | Operational | No | |
| Efficiency Problems | Operational | No | |
| Physical Damage | Environmental | Limited (detectable via performance impact) | Sim (visual inspection) |
| Contamination/Mixing | Environmental | Limited (impact on performance via current analysis) | Sim (insulation test, visual inspection) |
Detectable faults
| Artesian e-MCM (Test Online) | Traditional Offline/De-energized Test |
| – Defects in rotor bars (via ESA) | – Insulation failure in stator windings (via IR, PI, BUT) |
| – Short-circuited stator turns (via ESA) | – Short-circuited stator turns (via surge tests) |
| – Eccentricity (via ESA) | – Open circuits (via continuity test) |
| – Harmonic Distortion (via power quality analysis) | – Physical damage (via visual inspection) |
| – Power Quality Issues | – Contamination/mixture (via IR, visual inspection) |
| – Efficiency Problems (via analysis of energy consumption) | – Loose connections (via continuity test, visual inspection) |
| – Pump performance issues (e.g., cavitation, clogging/obstruction) | – Rotor faults (via RIC) |
Main characteristics of different types of test
| Artesian e-MCM (Test in operation) | Traditional Offline/De-energized Test | |
| Physical Parameters | Measures voltage, current, power factor, crest factor, phase angles; high frequencies (10 kHz), high resolution power spectral density. | Measures insulation resistance, winding resistance, inductance (RIC) |
| Automatic Reports | Automatic reports with failure trends, times until failure, corrective actions, impact energy. | Manual/semi-automatic reporting; detailed but requires greater interpretation from the reader. |
| Impact of Unavailability | No unavailability; monitoring continues without operational interruption. | Requires scheduled stops; tests require longer duration (e.g., AND, outbreak, RIC). |
| Ease of Use | No sensor, installed on the engine control board; self-learning reduces false alarms. | Greater configuration (e.g., disconnect engine, manual rotor rotation for RIC); requires higher level of experience. |
| limitations | Limited static fault detection (e.g., insulation failure, open circuits). | Undetectable operational faults (e.g., harmonics, efficiency problems); implies mandatory unavailability. |
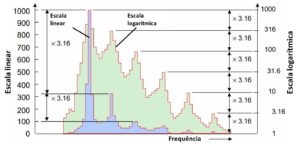
Characteristic breakdown frequencies